This page is under construction!
Main research areas
Fracture mechanical stress analysis and safety assessment of components
Fundamental and applied research in the fields of strength of materials and fracture mechanics to assess the safety, reliability and service life of technical constructions in energy technology, mining engineering, environmental technology and microsystems technology. Further development of failure criteria and fracture mechanics assessment concepts.
Mechanics of materials and damage mechanics
Theoretical modelling and numerical simulation of microstructural processes of deformation and failure of technical and geological materials using methods of material mechanics and damage mechanics. Application for the assessment and optimisation of material properties during production and under complex technical operating conditions, in particular the brittle and ductile failure behaviour of metals, ceramics and semiconductors.
Adaptive mechanical systems
Innovative disciplines in mechanical engineering (mechatronics, adaptronics, automation technology) aim to achieve adaptive, self-controlling behaviour of mechanical systems by integrating sensor, actuator, control and microtechnical components. These developments are supported by simulating the coupled mechanical, thermal and electromagnetic behaviour of the adaptive systems and the intelligent materials used. In particular, the fracture, fatigue and damage behaviour of piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials is being investigated.
Numerical calculation methods in solid mechanics
Further development of numerical calculation methods in solid mechanics (finite element method, boundary element method) for fracture mechanics stress analysis, simulation of crack propagation, implementation of damage laws and treatment of coupled field problems.
Development of miniaturised test methods
The aim is to determine the deformation and failure behaviour of materials using very small samples in the millimetre range, in particular the small punch test. This is necessary and advantageous when i) little sample material is available, ii) high property gradients exist and iii) local information is required. Typical fields of application are microelectronic materials, radiation-brittle steels, surface-treated metals, welded joints, thin films or composite materials.
Current and completed research projects

Concept and development of the large-scale HTEL module
DFG-SFB 920: Thermal shock and pressure flow behaviour of ceramic filter materials

Constraint effect with fault-tolerant design
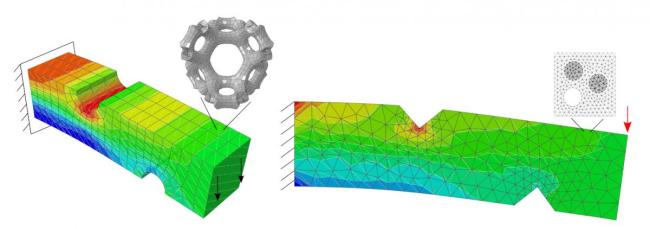
MonolithFE2
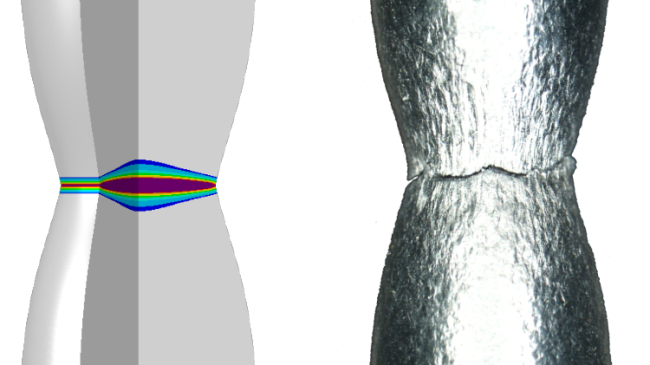
Non-local GTN model