Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnologie
Materials determine our lives! High-performance steels in cars can save our lives in an emergency, lightweight materials save millions of tonnes of oil, and modern communication systems would be inconceivable without high-performance materials, for example in electronics. In order to manufacture these products, the properties of the materials used must be matched to the respective application. It is therefore important to know what influences the material properties and how materials with the desired properties are manufactured. From glass, ceramics, plastics and metals to composites or semiconductor materials, the range of materials is so broad that students have to focus on specific groups in a single degree programme. The focus is therefore on metallic materials and semiconductor materials.
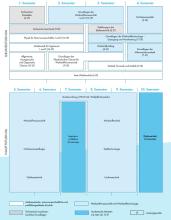
In the foundation course (1st to 4th semester), students learn the basics of physics, chemistry and engineering as well as materials science and materials technology. The relationships between the manufacturing process, the internal structure of the materials and the material properties are presented and the conditions for the efficient use of materials are explained. As the production of materials is geared towards their processing and utilisation, these relationships are illustrated during the course using various examples. 20 per cent of the courses are therefore practicals.
In the course of the degree programme, the entire chain from material production to use and recycling is considered in order to ensure the sustainable use of our raw materials, including secondary raw materials in recycling.
In the main course, students complete one of six possible fields of study and can specialise according to their personal interests and career goals. In the 7th semester, students complete a five-month internship in industry or at a research institution. Finally, the diploma thesis marks the successful completion of the diploma programme.
Fields of study
Materials science
Students learn how the properties of metallic and ceramic materials as well as the properties of semiconductors are related to their crystal structure and microstructure. In particular, principles are taught on how the properties of these materials can be specifically adjusted by designing their microstructure with the help of physical and chemical processes.
Materials engineering
This field of study focuses on the behaviour of materials in operational use as well as component design measures such as heat treatment, surface technology, corrosion protection and joining technology.
Non-ferrous metallurgy
Students learn about the technologies used to produce non-ferrous metals, their applications and areas of use, as well as issues relating to sustainable use and recycling.
Steel technology
Students acquire knowledge and skills relating to the fundamentals and technologies for the production of pig iron and steel, steel materials and their optimisation for different fields of application.
Foundry technology
Students are taught all the key aspects of modern foundry engineering - including knowledge of casting and moulding processes, casting materials and the sequence of processes in foundries.
Forming technology
Students learn about forming processes and the interactions between the forming process, forming behaviour and property development of metallic materials. The course also focuses on the modelling and simulation of forming processes and the development of new system concepts.
- Faculty
-
Faculty of Materials Science and Technology (Faculty 5)
- Degree
-
Diploma (Dipl.-Ing.)
- Standard period of study
-
10 Semester
- Part-time possible
-
Yes
- Start of studies
-
Winter semester
- Admission requirement
-
Abitur or subject-specific higher education entrance qualification or an entrance qualification recognized as equivalent
Language requirement
- Application: with at least B1 level German
- Admission to the degree program: with C1 level German (e.g. DSH-2)
- language courses and DSH exam at TUBAF
- Prep Courses (Studienkolleg)
- Course language
-
German
Material production, processing, application, development: e.g. development and production engineer, quality assurance
Other fields of activity: e.g. public service in federal and state authorities, employers' liability insurance associations, private and public testing institutes
Why study Materials Science and Technology at TUBAF?
Students find the best study conditions thanks to solid professional support. State-of-the-art equipment and laboratory facilities are available to them. Students have the opportunity to be involved in scientific work at an early stage as student assistants and to work closely with doctoral students on research into new composite materials.
The close link between manufacturing technologies, material properties and applications as well as the internal structure of the materials practised in Freiberg is unique at German universities. This understanding in particular is an essential prerequisite for a successful graduate engineer in the field of materials science and materials technology. And this is precisely where the degree programme in Freiberg differs significantly from other universities in Germany.
Materials science combines chemistry, physics and mathematics in a unique way by explaining the behaviour of materials at an atomic level.
Dipl.-Ing. Lea Haus - Engineer for Materials Science and Technology, PhD at Bosch Manufacturing Solutions in Stuttgart
The end-to-end view of value chains taught at TU Bergakademie Freiberg offers enormous future potential for graduates across all industries.
Dr Julia Hufenbach - Professor of Materials Functionalisation at TU Bergakademie Freiberg and research group leader at IFW Dresden
Image video
The world of materials - engineering studies at TUBAF
Rankings